Category:OSWe8eada7338114bbe8f65f6ee089d439f: Difference between revisions
([bot] update of page content) Tag: Metadata slot edit |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Overview== | |||
Zinc-air batteries are a type of {{Template:Viewer/Link|page=Category:OSW9cfcb1d3ed39476a930047ffb6de6cf0|url=|label=metal-air battery}} technology that offers the potential for high {{Template:Viewer/Link|page=Category:OSW4aa1b96e44a04b1aa0ac723d0223d80b|url=|label=energy density}}, inherent safety, and the use of affordable, earth-abundant materials. These characteristics have attracted interest for a wide range of energy storage applications, from hearing aids and sensors to large-scale stationary energy storage. Most zinc-air batteries commercially available today are {{Template:Viewer/Link|page=Category:OSW3b0b0d6e8b0e4491885e8421d3eb3b69|url=|label=primary cells}} (single-use), but there is growing research and development effort aimed at making zinc-air batteries {{Template:Viewer/Link|page=Category:OSWefc38420ecbb42e4bb3f208e7c417098|url=|label=secondary cells}} (rechargeable). This work is driven by the technology's promise to combine high performance with sustainability and low cost. | |||
==Working Principle== | |||
A typical zinc-air battery couples an oxygen reduction cathode with a zinc-based anode in an {{Template:Viewer/Link|page=Category:OSW615cff2abe954e65947198db23f4c878|url=|label=alkaline electrolyte}}. During the discharging process, oxygen from the air undergoes reduction at the cathode, while zinc metal at the anode is oxidized. In primary zinc-air batteries, the cathode is a porous gas diffusion electrode containing an oxygen reduction catalyst, such as manganese dioxide (MnO₂). The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) proceeds according to: | |||
O₂ + H₂O + 4e⁻ ⇌ 4OH⁻ | |||
Rechargeable (secondary) zinc-air batteries use a bi-functional air electrode capable of both the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) during discharge and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) during charging. | |||
{{Template:Viewer/Media | |||
| image_size = 300 | |||
| mode = default | |||
| textdata = File:OSWd16c853933b64ebe9fe640d5a74e96f6.png{{!}}A schematic showing the working principle of an alkaline zinc-air battery cell. Reused with permission from N. Borchers, S. Clark, B. Horstmann, K. Jayasayee, M. Juel, and P. Stevens, “Innovative Zinc-Based Batteries,” J. Power Sources, 484, no. December 2020, p. 229309, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229309.; | |||
}} | |||
| jsondata | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{ | { | ||
"rdf_type": [ | "type": [ | ||
" | "Category:OSW57beed5e1294434ba77bb6516e461456" | ||
], | |||
"metaclass": [ | |||
"Category:OSW57beed5e1294434ba77bb6516e461456" | |||
], | |||
"restrictions": [ | |||
{ | |||
"uuid": "55866785-b333-4724-9a94-7f4719846b19", | |||
"rdf_type": "owl:Restriction", | |||
"on_property": "Property:echem:hasNegativeElectrode", | |||
"some_values_from": "Category:OSWd0a26dc2fde94a11ac267c18499d28a5" | |||
} | |||
], | |||
"subclass_of": [ | |||
"Category:OSW9cfcb1d3ed39476a930047ffb6de6cf0", | |||
"Category:OSWe1d7fb0003b946ea90c9501f538dfc11" | |||
], | ], | ||
"uuid": "e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f", | "uuid": "e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f", | ||
"label": [ | "label": [ | ||
{ | { | ||
| Line 18: | Line 31: | ||
} | } | ||
], | ], | ||
"rdf_type": [ | |||
"owl:Class" | |||
], | |||
"iri": "https://w3id.org/emmo/domain/battery#battery_e8eada73_3811_4bbe_8f65_f6ee089d439f", | |||
"name": "ZincAirBattery", | |||
"meta": { | "meta": { | ||
"uuid": "ee6dfa71-7311-4c44-b90a-662a9fe01669", | "uuid": "ee6dfa71-7311-4c44-b90a-662a9fe01669", | ||
| Line 28: | Line 46: | ||
] | ] | ||
}, | }, | ||
"imported_from": "battery:battery_e8eada73_3811_4bbe_8f65_f6ee089d439f", | "imported_from": "battery:battery_e8eada73_3811_4bbe_8f65_f6ee089d439f", | ||
"altLabel": [ | "altLabel": [ | ||
{ | { | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
"lang": "en" | "lang": "en" | ||
} | } | ||
], | |||
"image": "File:OSW921ee64cb7494f7db2971219d78a057c.jpg", | |||
"attachments": [ | |||
"File:OSWd16c853933b64ebe9fe640d5a74e96f6.png" | |||
] | ] | ||
} | } | ||
| jsonschema | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{} | { | ||
"@context": [ | |||
"/wiki/Category:OSW9cfcb1d3ed39476a930047ffb6de6cf0?action=raw\u0026slot=jsonschema", | |||
"/wiki/Category:OSWe1d7fb0003b946ea90c9501f538dfc11?action=raw\u0026slot=jsonschema" | |||
], | |||
"allOf": [ | |||
{ | |||
"$ref": "/wiki/Category:OSWe1d7fb0003b946ea90c9501f538dfc11?action=raw\u0026slot=jsonschema" | |||
} | |||
], | |||
"type": "object", | |||
"uuid": "e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f", | |||
"title": "ZincAirBattery", | |||
"title*": { | |||
"en": "ZincAirBattery" | |||
}, | |||
"description": "a type of metal-air battery with a zinc negative electrode", | |||
"description*": { | |||
"en": "a type of metal-air battery with a zinc negative electrode" | |||
}, | |||
"required": [ | |||
"type" | |||
], | |||
"properties": { | |||
"type": { | |||
"default": [ | |||
"Category:OSWe8eada7338114bbe8f65f6ee089d439f" | |||
] | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
Latest revision as of 11:43, 15 April 2025
| ZincAirBattery | |
|---|---|
| ID | OSWe8eada7338114bbe8f65f6ee089d439f |
| UUID | e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f |
| Label | ZincAirBattery |
| Machine compatible name | ZincAirBattery |
 |
|
| Statements (outgoing) | |
| Statements (incoming) | |
|
|
|
Description
a type of metal-air battery with a zinc negative electrode
| Category (Class) |
|---|
| OWL Class | |
|---|---|
| Imported fromA prefixed IRI defining this entry as a imported term. In OSW the prefix must be a registered imported ontology.<br>Definition: OWL Class | https://w3id.org/emmo/domain/battery#battery e8eada73 3811 4bbe 8f65 f6ee089d439f |
| RelationsRelations of this class to other classes, instances or literals (OWL Restrictions)<br>Definition: OWL Class |
hasNegativeElectrode ZincBasedElectrode |
| EmmoClass | |
|---|---|
| metaclass<br>Definition: Category (Class), EmmoClass | |
| Supercategories<br>Definition: Category (Class), OWL Class, EmmoClass |
|
| Alternative label<br>Definition: EmmoClass |
|
Overview
Zinc-air batteries are a type of metal-air battery technology that offers the potential for high energy density, inherent safety, and the use of affordable, earth-abundant materials. These characteristics have attracted interest for a wide range of energy storage applications, from hearing aids and sensors to large-scale stationary energy storage. Most zinc-air batteries commercially available today are primary cells (single-use), but there is growing research and development effort aimed at making zinc-air batteries secondary cells (rechargeable). This work is driven by the technology's promise to combine high performance with sustainability and low cost.
Working Principle
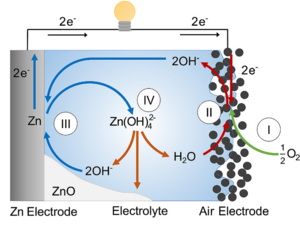
A typical zinc-air battery couples an oxygen reduction cathode with a zinc-based anode in an alkaline electrolyte. During the discharging process, oxygen from the air undergoes reduction at the cathode, while zinc metal at the anode is oxidized. In primary zinc-air batteries, the cathode is a porous gas diffusion electrode containing an oxygen reduction catalyst, such as manganese dioxide (MnO₂). The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) proceeds according to:
O₂ + H₂O + 4e⁻ ⇌ 4OH⁻
Rechargeable (secondary) zinc-air batteries use a bi-functional air electrode capable of both the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) during discharge and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) during charging.
A schematic showing the working principle of an alkaline zinc-air battery cell. Reused with permission from N. Borchers, S. Clark, B. Horstmann, K. Jayasayee, M. Juel, and P. Stevens, “Innovative Zinc-Based Batteries,” J. Power Sources, 484, no. December 2020, p. 229309, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229309.
jsondata
| type |
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| metaclass |
| |||||||||||
| restrictions |
| |||||||||||
| subclass_of |
| |||||||||||
| uuid | "e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f" | |||||||||||
| label |
| |||||||||||
| description |
| |||||||||||
| rdf_type |
| |||||||||||
| iri | "https://w3id.org/emmo/domain/battery#battery_e8eada73_3811_4bbe_8f65_f6ee089d439f" | |||||||||||
| name | "ZincAirBattery" | |||||||||||
| meta |
| |||||||||||
| imported_from | "battery:battery_e8eada73_3811_4bbe_8f65_f6ee089d439f" | |||||||||||
| altLabel |
| |||||||||||
| image | "File:OSW921ee64cb7494f7db2971219d78a057c.jpg" | |||||||||||
| attachments |
|
jsonschema
| @context |
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| allOf |
| |||||
| type | "object" | |||||
| uuid | "e8eada73-3811-4bbe-8f65-f6ee089d439f" | |||||
| title | "ZincAirBattery" | |||||
| title* |
| |||||
| description | "a type of metal-air battery with a zinc negative electrode" | |||||
| description* |
| |||||
| required |
| |||||
| properties |
|
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
O
- NeutralZincAirBattery (empty)
- AlkalineZincAirBattery (empty)